What is Cloud Computing? “Cloud computing is on-demand access to virtualized IT resources that are housed outside of your own data center, shared by others, simple to use, paid for via subscription, and accessed over the Web.”
Benefits
Enterprises are turning to cloud computing for the following reasons:
- Convenience: for fast procurement of on-demand IT services available on a self service basis from a variety of networked devices. Faster time to market.
- Adaptation/Elasticity: through the ability to mix and match IT services and increase or decrease their use as required.
- Innovation: cloud computing makes it easier to try new things while taking fewer risks via a PAYG business model (utility computing).
- Simplicity: cloud computing short-circuits IT complexity by reducing significant elements of the IT stack to standardized commodity services.
- Lower costs: from economies of scale based on IT resource pooling coupled with the PAYG business model to using these resources.
- Cost transparency/awareness: the ability to understand, measure, and manage who is using which IT resources at what cost for billing, planning, and optimization purposes.
- QoS: enterprises expect public and private cloud IT resources to be more reliable, available, scalable, and secure than traditional ones.
Definitions
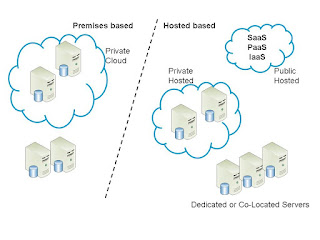
Private Cloud
Due to the limitations in terms of security and bandwidth, and the constraints in terms of application design and functionality of the various types of public cloud, some enterprise choose to keep their data center in their own premises and use similar cloud best practices. This means that enterprise take the capex burdon.
Public Cloud
Open Internet capabilities with data centers & services available over the internet.
Hybrid Cloud
A mix configuration of the other cloud flavors.
IaaS
Raw infrastructure, such as servers and storage, is provided from the vendor premises directly as an on-demand service: Amazon Web Services,…
PaaS
Development platforms hosted by the vendor, allowing developers to simply code and deploy without directly interacting with underlying infrastructure: Google AppEngine, Microsoft Azure, Force.com…
SaaS
Complete application systems delivered over the Internet on some form of "on-demand" billing system: Salesforce.com, Google Apps…
Strategy, how?
When Is Cloud Computing A Fit For The Enterprise
A couple of conditions need to be met before an enterprise decides to implement cloud strategy:
- Applications & processes have highly variable demand
- Internal data center limits are being reached
- Existing hardware has reached end of service life
- Speed of provisioning is constraining business execution
- Enterprise Datacenter no longer provides competitive advantage
Mix-Marketing 7C's Compass Model of Shimizu:
and the Enterprise Analysis 7S's from McKinsey:


No comments:
Post a Comment